Effects of Contraceptive Pills

The birth control pill also known as the contraceptive pill works by stopping sperm from joining with an egg. When sperm joins with an egg it is called fertilization. The hormones in the pill safely stop ovulation. No ovulation means there is no egg for sperm to fertilize, so pregnancy can't happen.
What are the types of birth control pills?
There are two different types of birth control pills. Both types contain hormones that prevent pregnancy.
-
Combination pills contain estrogen and progestin.
-
Progestin-only pills are also called “the minipill.” They are better for some women, such as those who are breastfeeding or have a history of blood clots and strokes, and should not take estrogen.
Side effects and risks
While birth control pills are safe for most women, they do come with some side effects and risks. Every woman reacts differently to the hormones in birth control pills. Some women have side effects, such as:
Decreased sex drive
Nausea
Bleeding between periods (abnormal menstruation)
Breast tenderness or swelling
Headache
Irritability or moodiness
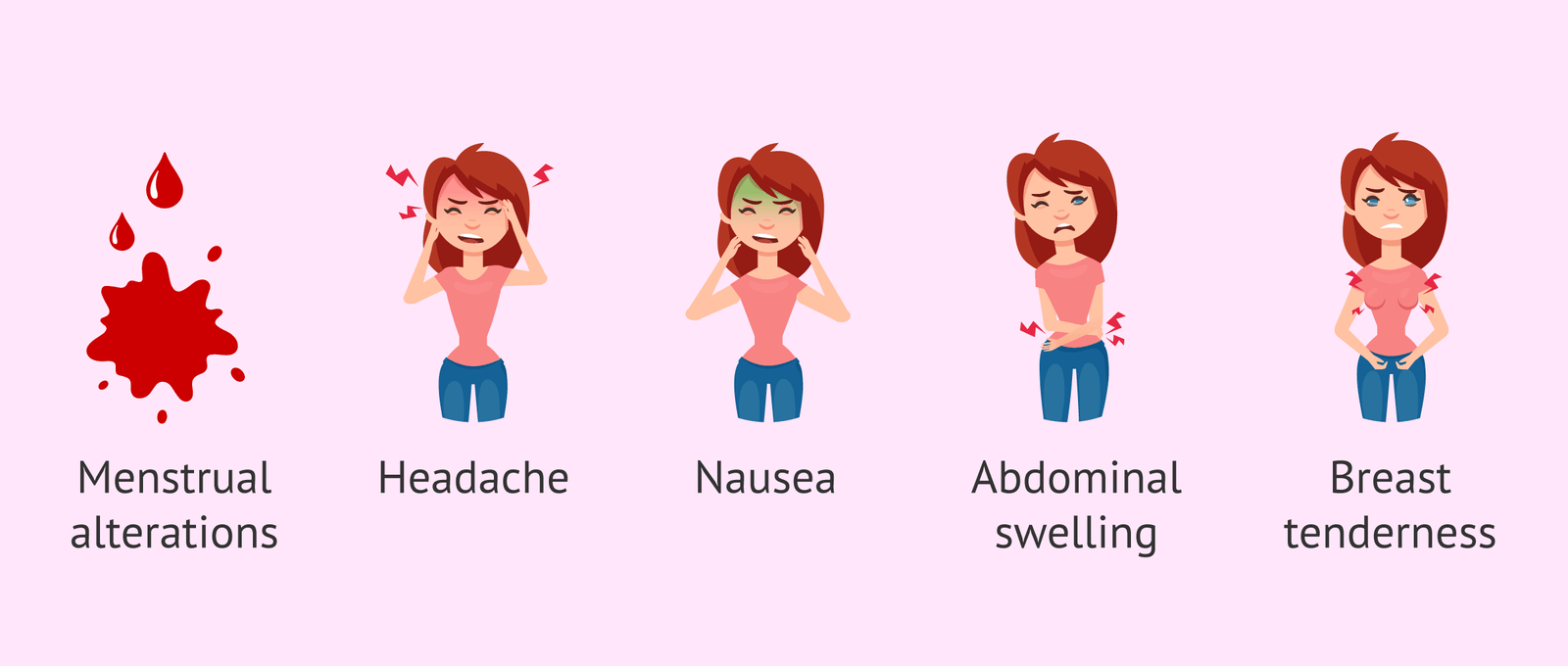
If you have these side effects, they will likely improve after a few months of using the pill. If they do not improve, talk to your doctor. They may suggest that you switch to a different type of birth control pill.
Risks
A serious risk of using birth control pills, especially combination pills, is an increased risk of blood clots. This can lead to:
Blood clots
deep vein thrombosis
heart attack
hypertension (high blood pressure)
stroke
pulmonary embolism
Overall, the risk of a blood clot from using any kind of birth control pill is low. According to the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 0.1% of women will develop a blood clot after taking a combination pill for a year. This risk is still lower than the risk of developing a blood clot during pregnancy and immediately after giving birth.
However, the risk of a blood clot from the pill is higher for certain women. This includes women who:
are very overweight
have high blood pressure
- are on bed rest for long periods

All hormonal contraceptives are associated with changes in menstrual bleeding patterns. When beginning a new hormonal contraception method, some women may experience irregular bleeding or spotting. Others may notice changes in the length or heaviness of bleeding, and some may stop bleeding entirely. (For reference, women who are not using hormonal contraception experience an average of 6 to 7 bleeding or spotting days per month.)
Acupuncture perspective
When a woman comes off the birth control pill after being on it for a long time, usually, the periods do not return for a long time. In practice, it is observed that, many times when a woman’s periods may not return for over a year after being on the pill for some years. The birth control pill causes a Blood deficiency and a Kidney deficiency and those are the reasons why the periods do not return. In such cases, the treatment to regularize the period is more difficult and it requires a longer period.
In some women, when they come off the pill, it is observed that their period returns after a couple of months but with an average of 1 or 2 days of bleeding or spotting. This is an alarming condition. This indicates that blood is deficient, and if this is not addressed and continues for a long time, will eventually cause serious health conditions at a later stage.
The change in the menstrual cycle affects the physical and emotional health of the women. Along with physical health conditions, they may also experience weakness, lassitude, listlessness, lack of enthusiasm, mood swings, irritation, anger, frustration, etc.
Both the physical and emotional effects of the long-term use of birth control pills can be effectively treated with acupuncture without any side effects. An expert acupuncturist can diagnose the underlying condition and work out a treatment and diet plan to combat this situation.
To summarize, it is advisable to choose an appropriate contraceptive method in consultation with your partner and doctor to minimize the effects on the women’s health in the long run.
Stay tuned to read more upcoming articles.
Shripad Chodankar
May 6, 2021




